
Interest is then charged on the principal for a loan, while an investor might earn money based on the principal that they invested. If rates decrease, your mortgage will be paid off faster.Ī principal is the original amount of a loan or investment. This will cause your mortgage to be paid off slower than scheduled. This will reduce the amount of principal that is being paid. If interest rates rise, more of your mortgage payment will go towards interest. While the monthly mortgage payment for a variable-rate mortgage does not change, the portion going towards interest will change. On the other hand, variable-rate mortgages have a mortgage interest rate that can change. Your principal will be paid off at an increasingly faster rate as your term progresses. Fixed-rate mortgages have an interest rate that does not change. This behaviour can change depending on your mortgage type. This is why your initial monthly payment will have a larger proportion going towards interest compared to the interest payment near the end of your mortgage term. However, since your monthly mortgage payment stays the same, this means that the amount being paid towards your principal will become larger and larger over time. A smaller principal balance will result in less interest being charged. Your regular mortgage payments will stay the same for the entire length of your term, but the portions that go towards your principal balance or the interest will change over time.Īs your principal payments lower your principal balance, your mortgage will become smaller and smaller over time. In addition, you’ll receive an in-depth schedule that describes how much you’ll pay towards principal and interest each month and how much outstanding principal balance you’ll have each month during the life of the loan.When you make a mortgage payment, you are paying towards both your principal and interest. The calculator will tell you what your monthly payment will be and how much you’ll pay in interest over the life of the loan. You can also add extra monthly payments if you anticipate adding extra payments during the life of the loan. To use the calculator, input your mortgage amount, your mortgage term (in months or years), and your interest rate. Figure out how much equity you have in your home.See how much interest you have paid over the life of the mortgage, or during a particular year, though this may vary based on when the lender receives your payments.
#30 YEAR MORTGAGE CALCULATOR FULL#

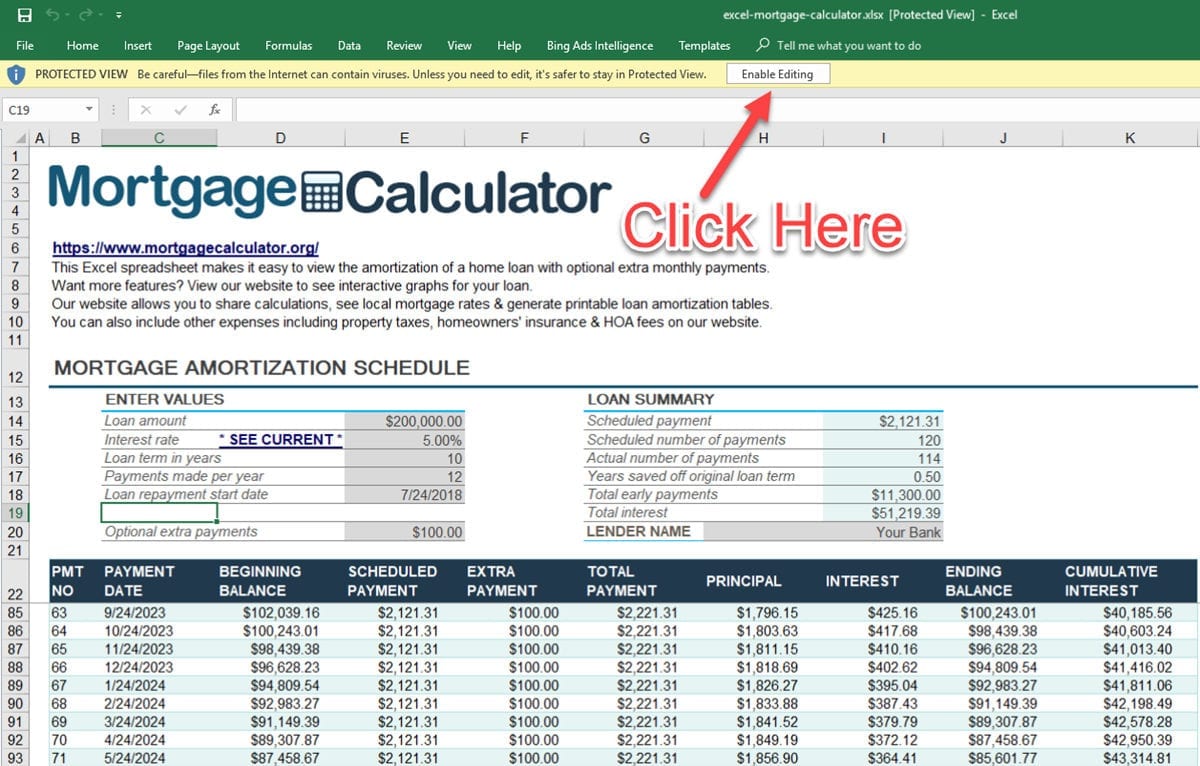
Initially, most of your payment goes toward the interest rather than the principal. The downside is that you’ll spend more on interest and will need more time to reduce the principal balance, so you will build equity in your home more slowly. With a longer amortization period, your monthly payment will be lower, since there’s more time to repay. Over the course of the loan, you’ll start to have a higher percentage of the payment going towards the principal and a lower percentage of the payment going towards interest. If you take out a fixed-rate mortgage, you’ll repay the loan in equal installments, but nonetheless, the amount that goes towards the principal and the amount that goes towards interest will differ each time you make a payment. Over the course of the loan term, the portion that you pay towards principal and interest will vary according to an amortization schedule.
#30 YEAR MORTGAGE CALCULATOR PLUS#
Each month, your mortgage payment goes towards paying off the amount you borrowed, plus interest, in addition to homeowners insurance and property taxes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
